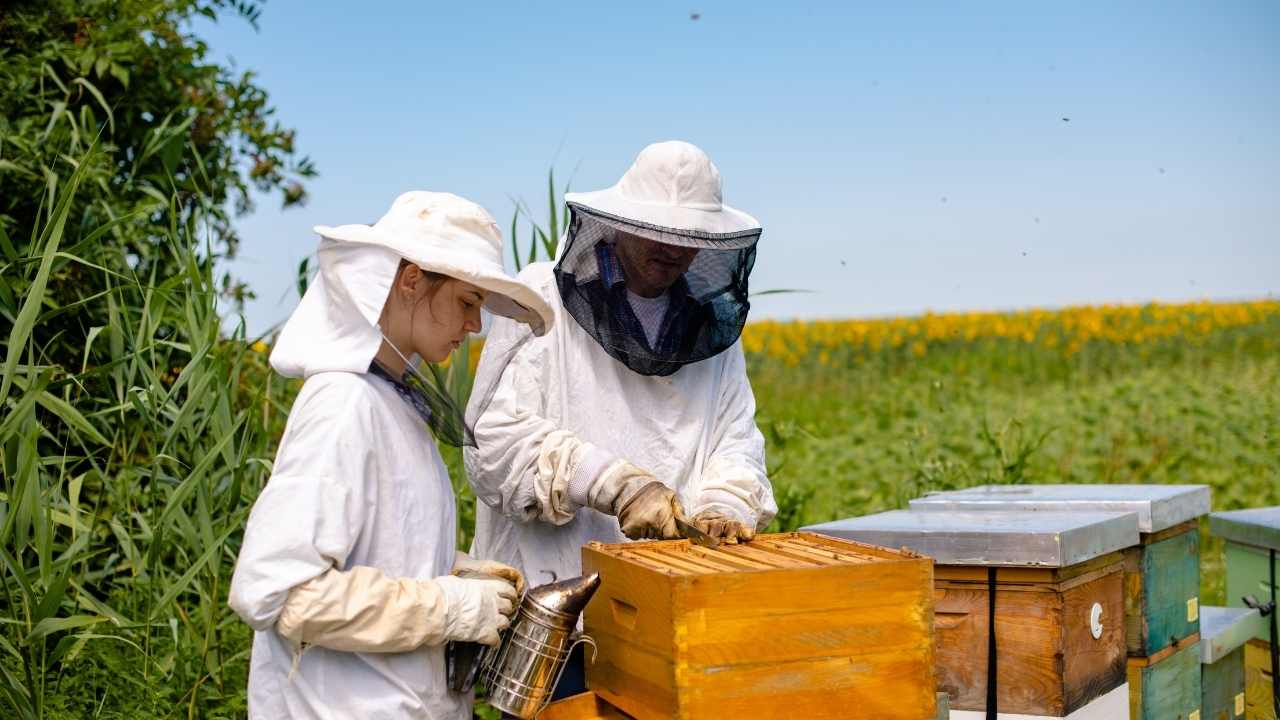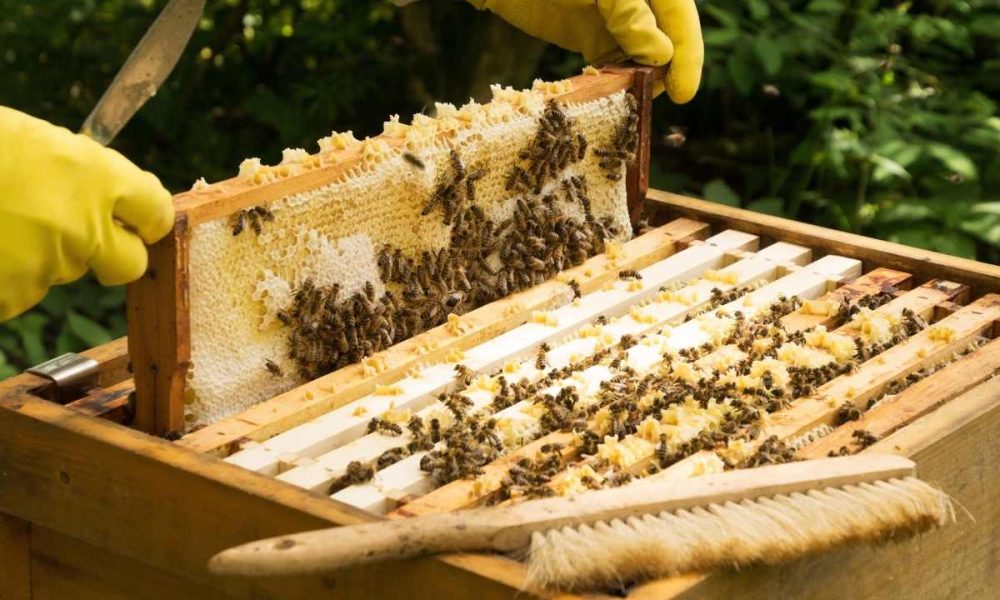
Imagine a world without the buzzing of bees. A world where flowers don’t bloom, fruits don’t grow, and food is scarce. It’s like a symphony without its conductor or a puzzle missing its crucial piece. Bees play an essential role in our ecosystem, pollinating crops that make up one-third of our global food supply. They are the unsung heroes that keep our planet alive and thriving.
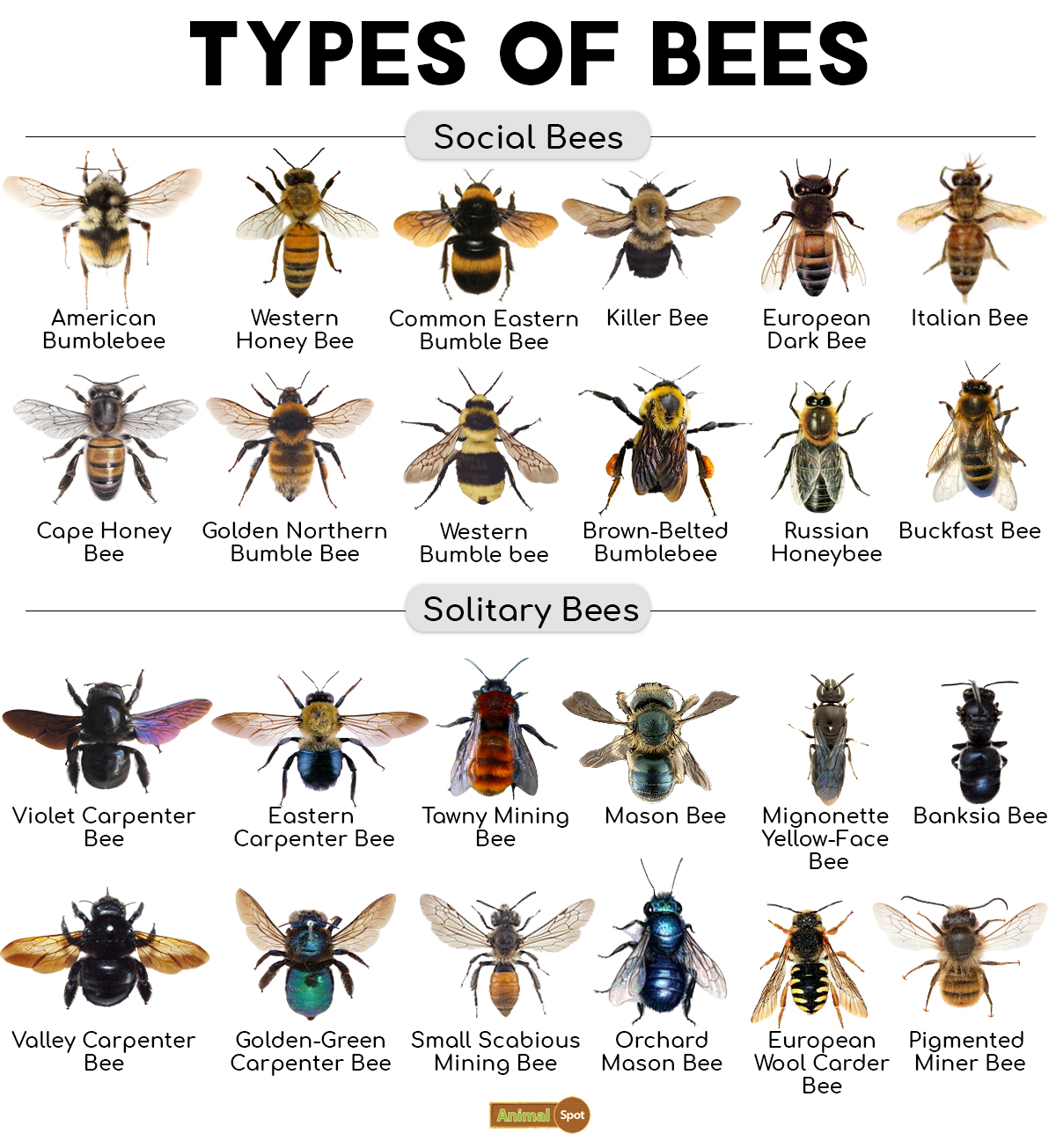
In this article, we will take a closer look at three species of bees: Apis Mellifera, Apis Cerana, and Apis Dorsata. These tiny creatures might seem insignificant to some, but they hold immense power in their wings. Through this exploration, we hope to shed light on the fascinating world of bees and their vital role in sustaining life on earth. So buckle up for an exciting journey into the bee kingdom!
Introduction to the Importance of Bees in Our Ecosystem
You probably don’t realize just how crucial bees are for our planet’s well-being, but without them, we’d be in a lot of trouble. Bees play an essential role in pollinating plants and crops that sustain the global food supply. In fact, one-third of the world’s food production is reliant on bee pollination, making it worth over $200 billion annually.
Unfortunately, bee populations have been declining due to habitat loss, pesticides, climate change and disease. This decline not only affects the bees themselves but also has a significant impact on agriculture and food production. Without bees to pollinate plants and crops, many fruits and vegetables would cease to exist or become much more expensive due to their limited supply. Therefore, it is important to understand the different types of bees that exist and how they contribute to our ecosystem. With that in mind, let’s take a closer look at Apis mellifera: the Western honey bee.
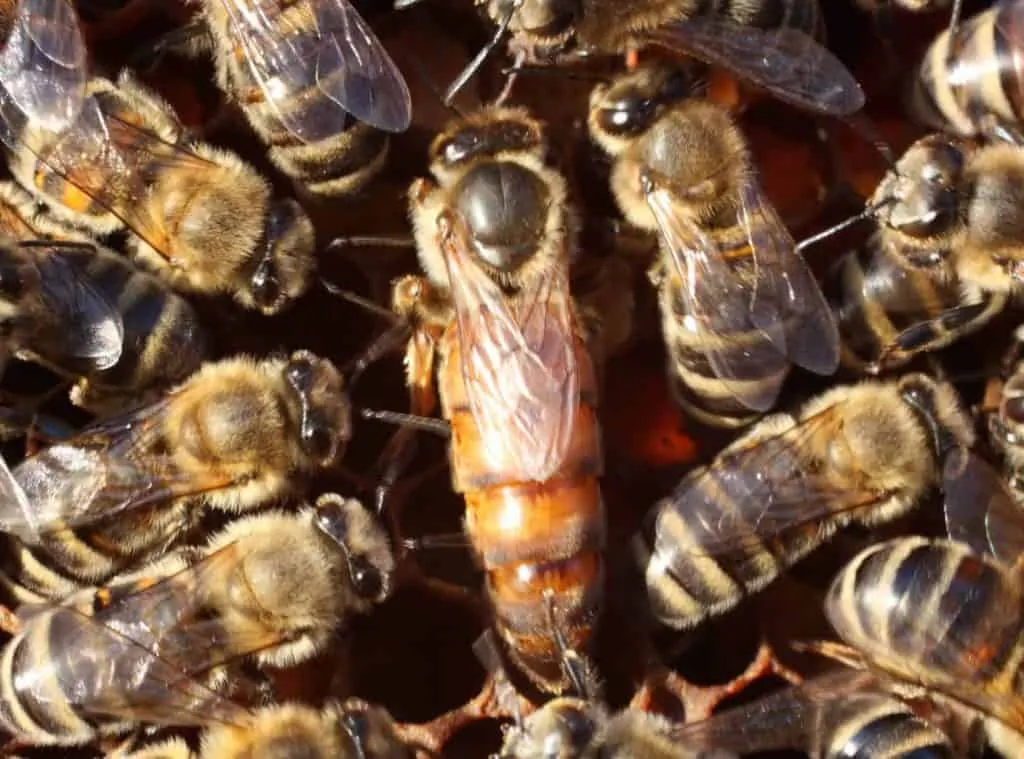

Apis Mellifera: The Western Honey Bee
Hey, you know that little yellow and black insect that makes all that delicious honey? Well, let me tell you about the Western Honey Bee, also known as Apis mellifera. This species is an important pollinator and producer of honey for humans. They are highly social insects, living in colonies with a queen bee who lays eggs and workers who collect nectar and pollen to feed the colony.
One of the unique characteristics of Apis mellifera is their ability to communicate with each other through a dance called the waggle dance. This dance tells other bees where to find food sources based on distance and direction. In addition to their importance in pollination and honey production, Apis mellifera are also used in scientific research due to their complex social behavior. However, climate change is affecting these bees by altering blooming times of flowers they rely on for food and increasing temperatures which can affect colony survival rates.
Now let’s move on to learn about another important bee species: apis cerana, or the eastern honey bee.
Apis Cerana: The Eastern Honey Bee
So, you’re interested in learning about Apis Cerana, the Eastern Honey Bee? Well, this species is native to Asia and plays a crucial role in pollination of various crops such as coffee, mangoes, and lychees. What sets them apart from other bees is their unique ability to build nests in trees and shrubs rather than hives.
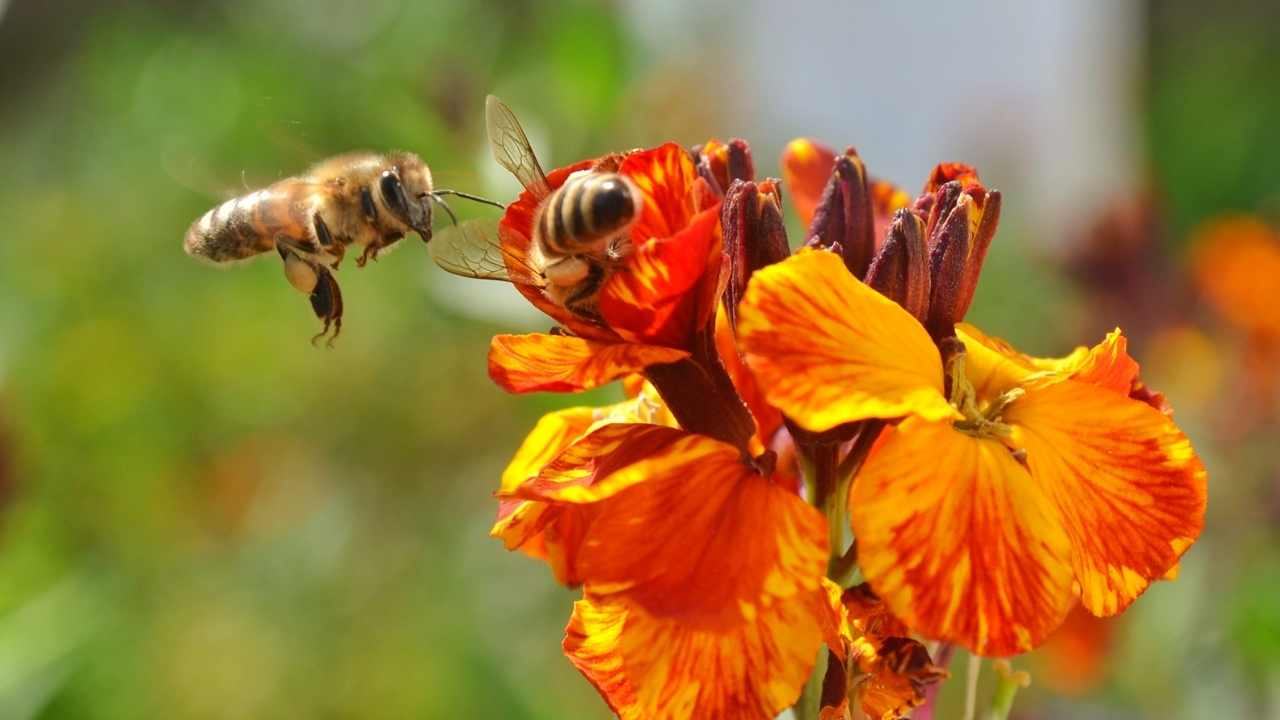

Native to Asia
These incredible pollinators have been thriving in Asia for centuries. Apis cerana, commonly known as the Eastern honey bee, is native to the region and has a rich evolutionary history that dates back to millions of years ago. They are smaller in size compared to their western counterparts, Apis mellifera, and have a distinct black abdomen with yellow stripes.
Distribution patterns of Apis cerana vary across different parts of Asia. They can be found in countries such as India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar and many more. However, due to human interference and habitat destruction, their populations have been declining rapidly over the years. Despite this decline in numbers though, they play a crucial role in pollination which we will explore further next.
As you move on from understanding the distribution patterns of Apis cerana though it is important to realise that these bees are vital pollinators for various crops including fruits like mangoes and lychees as well as vegetables such as cucumber and pumpkin.
Importance in Pollination
Pollination is crucial for crop growth and productivity, and did you know that honey bees alone contribute to over $15 billion worth of crops in the United States each year? Bees play a vital role in pollinating fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Without them, many crops would not be able to produce fruit or yield enough harvests. Some benefits of bee pollination include:
- Increased fruit size and quality
- More uniform ripening
- Higher yields
- Better resistance to pests and diseases
- Improved shelf life
However, there are also challenges that come with relying on bee pollination. Colony collapse disorder (CCD) has led to the loss of millions of bees around the world. Pesticide use can harm bees’ reproductive systems and ability to navigate back to their hives. Climate change affects flower blooming times and disrupts natural cycles. Despite these obstacles, it’s clear that bees are essential for our food supply chain.
As we continue our exploration of Apis mellifera, Apis cerana, and Apis dorsata, let’s dive into their unique characteristics that make them so important in the world of pollinators.
Unique Characteristics
Let’s explore what sets these amazing pollinators apart and makes them stand out from the rest! One of the most distinct features of the Apis species is their physical anatomy. For example, the Apis mellifera has a long tongue that allows them to access nectar in deep flowers, while Apis cerana has a unique ability to fly at high altitudes due to their efficient respiratory system. Additionally, all three species have multiple eyes that allow them to see polarized light and navigate using the sun’s position.
In terms of behavioral patterns, each species has its own unique quirks. The Apis mellifera is known for their complex social hierarchy where each bee has a specific role within the hive. Meanwhile, Apis cerana has adapted to living in areas with predators by developing a defense mechanism that involves swarming around intruders and heating up their bodies through rapid wing movement. Understanding these physical and behavioral differences can help us appreciate how diverse and fascinating these creatures truly are! Speaking of diversity, let’s move on to our next topic about apis dorsata: the giant honey bee.

Apis Dorsata: The Giant Honey Bee
As you delve deeper into the world of honey bees, it’s time to turn your attention to Apis dorsata: the giant honey bee. This is the largest species of bee, found in South and Southeast Asia. With unique characteristics that set it apart from other species, studying this impressive insect can reveal insights into the complex world of bees and their crucial role in our ecosystem.
Largest Species of Bee
You’ll be astonished by the sheer size of this buzzing giant, towering over its smaller counterparts and dominating the landscape with its impressive wingspan. The Apis dorsata, also known as the giant honey bee, is the largest species of bee in the world. Here are three things you need to know about this majestic insect:
-
Ecological impact: As pollinators, these bees play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by facilitating growth and reproduction of plants.
-
Behavior patterns: Unlike other honey bees, Apis dorsata colonies build their nests on high tree branches or cliffs for protection against predators such as bears and humans.

-
Honey production: These bees produce large quantities of honey which is harvested by local communities in South and Southeast Asia.
Found in South and Southeast Asia, these fascinating creatures have adapted to their environment through their unique nesting behavior and ecological impact on local plant life.
Found in South and Southeast Asia
The sheer beauty and diversity of the flora and fauna in South and Southeast Asia is nothing short of breathtaking. Among the many species that call this region home are three types of bees: Apis mellifera, Apis cerana, and Apis dorsata. Unfortunately, these bees are facing numerous challenges due to habitat destruction caused by human activities such as deforestation and land-use changes.
Conservation strategies have been put in place to protect these important pollinators. For example, efforts are being made to restore degraded habitats to provide sufficient foraging areas for the bees. Additionally, education and outreach programs are being implemented to raise awareness about the importance of bee conservation among local communities. Despite these efforts, much work needs to be done if we hope to ensure the survival of these incredible creatures for future generations.

As we move into discussing their unique characteristics, it’s important to remember that protecting their habitats is crucial for ensuring their continued existence on this planet.
Unique Characteristics
You can gain a deeper understanding and appreciation of the remarkable traits possessed by these pollinators found in South and Southeast Asia. One of the most interesting aspects of Apis mellifera, Apis cerana, and Apis dorsata is their physical adaptations. For instance, A. dorsata has long legs that help them build their large honeycombs on high tree branches, while A. cerana has a special gland that produces an enzyme that protects their hives from harmful bacteria.
In addition to their physical adaptations, these bees also exhibit unique behavioral characteristics. All three species have highly advanced communication systems that allow them to work together effectively in finding nectar sources and building their colonies. Moreover, they are able to navigate through complex environments using various cues such as the position of the sun or landmarks around them. These fascinating traits make them not only great pollinators but also important contributors to our ecosystem by maintaining biodiversity and supporting crop production.
The Role of Bees in Our Ecosystem
You probably know that bees are important in pollination, but did you know just how crucial this role is to the ecosystem? Bees help to pollinate around one-third of the food crops we eat and help maintain biodiversity in nature. Unfortunately, these industrious insects are facing threats to their population such as habitat loss, pesticide use and climate change. As a result, conservation efforts have become essential in ensuring the survival of bees and maintaining our fragile ecosystem.

Importance in Pollination
Pollination is vital for the survival of many crops and plants, and these three species of bees play a crucial role in ensuring that our ecosystems thrive. Without their pollination efforts, we wouldn’t have access to essential food items such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. The importance of these species lies in their ability to transfer pollen from male flowers to female flowers, which leads to fertilization and ultimately results in the production of fruits and seeds.
It’s not just humans who benefit from the work of these bees; other animals rely on them too. For instance, birds feed on insects that are attracted to flowering plants pollinated by bees. In contrast, small mammals consume fruits produced by plants that depend on bee pollination. If we lose these bees due to bee decline drivers such as habitat loss or pesticide use, entire ecosystems will be disrupted. We must take action now to protect these important creatures and ensure their survival for generations to come.
Threats to their population include various human activities like land-use changes leading to habitat destruction or fragmentation, overuse or misuse of pesticides leading to toxicity levels harmful for bees’ health causing death or disorientation during flight patterns while searching for food sources.
Threats to Their Population
Losing these crucial pollinators to habitat destruction and pesticide toxicity could have far-reaching consequences for entire ecosystems. The use of pesticides has been linked to the decline in bee populations, as they can affect both the bees’ health and their ability to navigate back to their hives. Habitat destruction, on the other hand, is caused by human activities such as deforestation and urbanization. This results in a loss of food sources for bees, as well as nesting sites and shelter.

The decline in bee populations is not only a concern for beekeepers but also for farmers who rely on them for crop pollination. Without bees, crops such as almonds, apples, and blueberries would be severely impacted. Therefore, it is important that we take action to address these threats to their population through conservation efforts that aim at preserving habitats and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Conservation Efforts
If you’re interested in helping to preserve the habitats and promote sustainable farming practices for these crucial pollinators, there are a variety of conservation efforts you can get involved in. Collaborative efforts between beekeepers, farmers, and government agencies have been successful in creating protected areas for bees to thrive and promoting pesticide-free farming practices. By supporting local beekeepers and purchasing organic produce from sustainable farms, you can directly contribute to the preservation of bee populations.
Government policies also play a crucial role in bee conservation. Some countries have implemented bans on harmful pesticides known to harm bees, while others offer financial incentives for farmers who adopt sustainable agricultural practices. By advocating for stronger legislation that protects bees and their habitats, you can help ensure a future where these important pollinators continue to thrive.
In conclusion: The fascinating world of bees is not only incredibly complex but also critical to our food supply chain. With threats such as habitat loss and pesticide use putting their populations at risk, it’s essential that we take action towards conservation efforts. Through collaborative efforts with beekeepers and government policies that prioritize sustainability over profit margins, we can work towards preserving the habitats of these amazing creatures for generations to come.
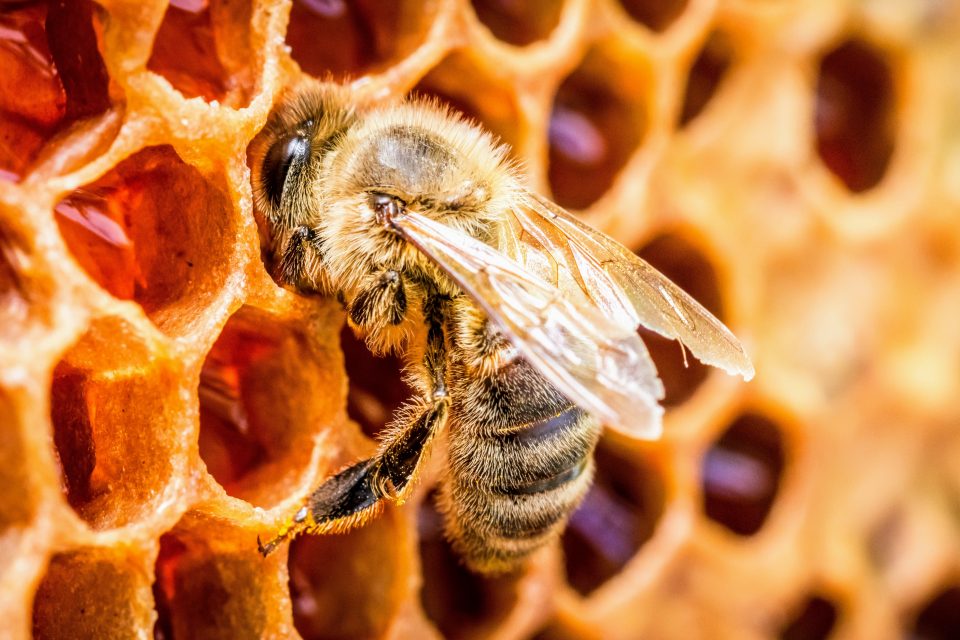

Conclusion: The Fascinating World of Bees
You may be surprised by the intricate social organization and communication methods of bees, which are truly fascinating to observe. Bees live in highly organized colonies with strict hierarchies and specialized roles for each individual. They use a variety of signals to communicate with one another, including pheromones, dances, and sounds. By studying these behaviors, researchers have gained valuable insights into how bees navigate their environment, find food sources, and protect their hives from predators.
In addition to being endlessly intriguing creatures to study, bees also play an important role in our world as pollinators. Without them, many of the foods we eat would not exist. Beekeeping has become a popular hobby among those who are interested in sustainable agriculture and supporting local ecosystems. By learning about bee behavior and taking steps to support their well-being through responsible beekeeping practices or simply planting pollinator-friendly plants in your garden or yard, you can help ensure that these incredible insects continue to thrive for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do honey bees communicate with each other?
When it comes to communication, honey bees have a complex system that relies on various types of signals. The most well-known type is the waggle dance, which involves a bee moving her body in a figure-eight pattern to indicate the location of nectar or pollen. But there are also pheromones, sounds, and physical contact used to convey information about food sources, danger, and other important issues. Each type of communication has its own effectiveness depending on the context, but they all play a crucial role in determining hive behavior. For example, if a scout bee communicates effectively about a new food source through her waggle dance or pheromones, more worker bees will be recruited to collect from that source. On the other hand, if an alarm pheromone is released due to perceived danger nearby, all bees in the vicinity will become alert and respond accordingly by defending the hive or fleeing. It’s remarkable how much these tiny creatures rely on effective communication for their survival and success as a colony.
What are the differences between honey bees and bumblebees?
You may think honey bees and bumblebees are the same, but they couldn’t be more different! While honey bees are known for their intricate communication system, bumblebees exhibit unique behavior that makes them stand out. Did you know that bumblebees can actually regulate their own body temperature? This incredible ability allows them to fly in colder temperatures than most other insects. Unfortunately, these amazing creatures are facing a decline in population due to habitat loss and pesticide use. Thankfully, there are conservation efforts underway to protect these fuzzy pollinators and ensure their survival for generations to come. So next time you see a bumblebee buzzing by, take a moment to appreciate all of the amazing things they do for our planet!

How do honey bees produce honey?
When it comes to honey production, the anatomy and foraging behavior of honey bees are key factors. Honey bees have specialized glands that produce enzymes that break down nectar into glucose and fructose, which they store in their bodies as food. They use their long tongues to collect nectar from flowers, and store it in a special stomach called the crop. Once back at the hive, worker bees regurgitate the nectar into other worker bees’ mouths to further break down the sugars. This process continues until the nectar is turned into honey, which is then stored in comb cells for later use by the colony. So next time you enjoy some delicious honey on your toast or in your tea, remember all of the hard work and intricate processes involved in producing this sweet treat!
What are the biggest threats to honey bee populations?
Picture yourself walking through a meadow on a sunny day. The sound of buzzing fills the air as you watch honey bees flit from flower to flower, gathering nectar and pollen to bring back to their hives. Unfortunately, this idyllic scene is under threat due to two major factors: pesticide exposure and habitat loss. Pesticides used in agriculture can be harmful to bees, causing confusion, disorientation, and even death. Meanwhile, urbanization and monoculture farming have reduced the availability of diverse food sources for bees while also destroying their nesting sites. If we don’t act now to address these threats, we risk losing not just the honey bee but also the vital role they play in pollinating crops that feed us all.
How do honey bees contribute to the pollination of crops worldwide?
You may not realize it, but honey bees are responsible for pollinating one-third of the food we eat. However, honey bee decline is a major concern due to factors such as habitat loss and pesticide use. This is why maintaining honey bee biodiversity is crucial in ensuring the health and productivity of our crops. Different species of honey bees, such as Apis mellifera, Apis cerana, and Apis dorsata have unique traits that allow them to efficiently pollinate different types of plants. By preserving these diverse species, we can ensure that crops worldwide receive the necessary pollination they need to thrive. It’s important to remember that by taking care of our honey bee populations, we’re ultimately serving ourselves and our communities by securing a sustainable food source for generations to come.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have now learned about the three amazing species of bees that play a vital role in our ecosystem. From the Western Honey Bee, Apis Mellifera, to the Eastern Honey Bee, Apis Cerana, and the Giant Honey Bee, Apis Dorsata, each species has its unique characteristics and behaviors that make them essential to our environment.

As you reflect on these fascinating creatures, you might be reminded of Emily Dickinson’s poem "To Make a Prairie," where she describes how nature works tirelessly behind the scenes to create beauty and balance in our world. Bees are an integral part of this system as they pollinate plants, produce honey and wax, and help maintain biodiversity. Without their efforts, many plant species would not thrive or even exist.
In conclusion, there is no doubt that bees are critical players in our ecosystem’s delicate web of life. By learning more about these incredible creatures like Apis Mellifera, Apis Cerana,and Apis Dorsata , we can appreciate their contributions better and take steps to protect them from threats such as habitat loss or pesticide use. Remember that every time you see a bee buzzing around your garden or park; it is doing important work for nature’s grand design.

Roger Thomas is a seasoned beekeeper and hive architect with a deep-seated passion for sustainable living. His fascination with bees has shaped his professional career, giving him practical and theoretical expertise in bee behavior, colony health, and optimal hive conditions. Roger’s technical skills shine in his bespoke hive creations that cater to the specific needs of diverse bee species, while his sustainable practices promote environmental balance and the wellbeing of the bee population.
As he continues his journey in beekeeping, Roger has become a dedicated advocate for responsible practices and an insightful educator in his field. His posts aim to inspire new beekeepers, underline the importance of sustainability, and showcase the remarkable contribution bees make to our ecosystem. Roger invites you to join him as he delves into the world of bees and the rewarding, honey-sweet art of beekeeping.


